Since
![]() , If we change one of the variables, (P, V, n, or T) then one or more of the
other variables must also change. This leads to the equation
, If we change one of the variables, (P, V, n, or T) then one or more of the
other variables must also change. This leads to the equation
![]() or if the number of moles stays the
same
or if the number of moles stays the
same
![]() .
.
Boyle’s Law:
Boyle’s Law examines the effect of changing volume on Pressure.
To isolate these variables, temperature must remain constant.
We can eliminate temperature from both sides of the equation and we are
left with P1V1= P2V2
![]()
Sample Problem: A piston with a volume of gas of 1.0 m3 at 100 kPa is compressed to a final volume of 0.50 m3. What is the final pressure?
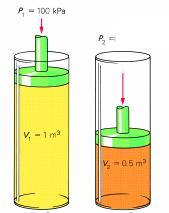
P1 is 100 kPa
V1 is 1.0 m3
V2 is 0.50 m3
P2 is unknown
Charles’s Law examines the effect of changing temperature on volume. To isolate these variables, pressure must remain constant.
![]() so Charles’s law is
so Charles’s law is
![]()
Sample problem: A piston with a volume of gas of 1.0 m3 at 273 K is cooled to a temperature of 136.5 K ? What is the final volume? (Assume pressure is kept constant.)
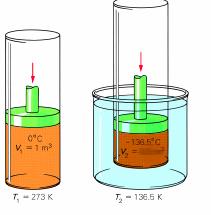
P1 is 100 kPa
V1 is 1.0 m3
V2 is 0.50 m3
P2 is unknown
Charles
law Applet See what happens when you increase temperature.
Increasing temperature __________ pressure.