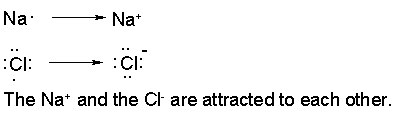
Please watch the animation 9.3 on your CD.
When a metal combines with a non-metal, the resulting bond is an ionic bond. The metal loses electrons and becomes positively charged and the non-metal gains electrons and becomes negatively charged. Positively charged ions are called cations, negatively charges ion are called anions.
Ionic bonds are formed between anions cations. It is the electrostatic attraction between opposite charges.
In sodium chloride, the sodium (symbol Na) loses an electron and becomes positively charged in its ionic state. All the metals in group I are +1 in their ionic state. All the metals in group II are +2 in their ionic state. You can find the charges of various metals in the chart below.
The chlorine (Cl) will gain an electron and becomes negaitvely charged in its ionic state. All the elements in group VII are -1 in their ionic state. All the metals in group VI are -2 in their ionic state. You can find the charges of various non-metals in the chart below.
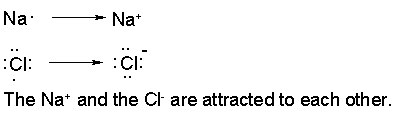
Charges of some Common Monatomic
ions
| H
1+ 1- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Li
1+ |
Be
2+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
3- |
O
2- |
F
1- |
|
| Na
1+ |
Mg
2+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al
3+ |
|
P
3- |
S
2- |
Cl
1- |
|
| K
1+ |
Ca
2+ |
Sc
3+ |
Ti
3+ 4+ |
V
3+ 4+ |
Cr
2+ 3+ |
Mn
2+ 3+ |
Fe
2+ 3+ |
Co
2+ 3+ |
Ni
2+ 4+ |
Cu
1+ 2+ |
Zn
2+ |
|
|
|
|
Br
1- |
|
| Rb
1+ |
Sr
2+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pd
2+ 4+ |
Ag
1+ |
Cd
2+ |
|
Sn
2+ 4+ |
|
|
I
1- |
|
| Cs
1+ |
Ba
2+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pt
2+ 4+ |
Au
1+ 3+ |
Hg
2+ * |
|
Pb
2+ 4+ |
|
|
|
|
| Fr
1+ |
Ra
2+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please note that
many of the metals shown here can have more possibilities that I can show here.
Vanadium, for example, can be 2+, 3+, 4+ or 5+.
I have only shown the more common charges.
*Mercury can be 1+ in the polyatomic ion Hg22+.